FAQ
Click on the question to get to the answers
What is infertility?
Is infertility a male or female problem?

If I had a baby once, can I still be infertile later?
- Increased age in the female causing decreased pool or reserve of eggs
- Blocked fallopian tubes, ovulatory dysfunction (Ovary may not be developing or releasing egg properly) , or other uterine conditions (Fibroids, polyp, adhesions, adenomyosis etc ).
- Declining sperm count and motility in the male.(which may have been normal or borderline the first time you conceived)
Hence if there is a difficulty in conceiving the second time, you should consider visiting a fertility specialist to get proper evaluation and treatment options.
What causes infertility?
There are numerous causes of infertility. They are broadly :
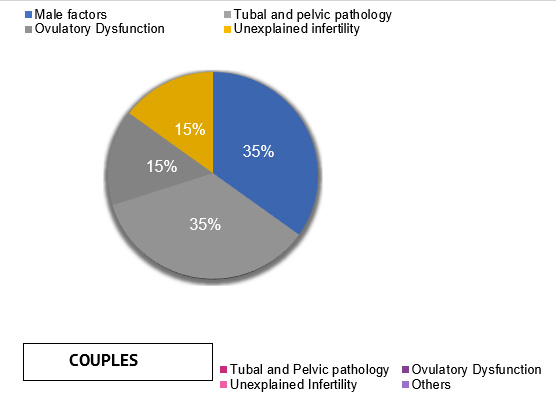
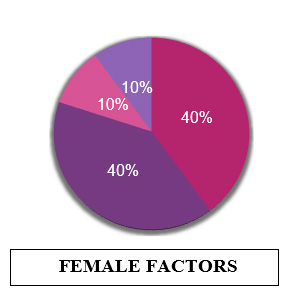
Ovulatory dysfunction (When the egg does not develop to its maturity or is not released from the ovary properly) -
- Polycystic ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
- Anovulation/ infrequent ovulation due to hypo/hyperthyroidism, hyperprolactinemia.
- Excess stress, weight gain, environmental factors, smoking
- Age related decreased ovarian reserve
- Premature ovarian insufficiency
Tubal and Pelvic pathologies :
- Tubal blocks and pelvic adhesions altering tubal anatomy and function due to pelvic inflammatory disease caused by infections such at tuberculosis, chlamydia, gonorrhoea .
- Endometriosis causing altered tuba-ovarian anatomy due to pelvic adhesions or chocolate cysts, decreased ovarian reserve, poor quality eggs.
- Uterine pathologies like endometrial polyps, fibroids, septum , intrauterine adhesions .
Male factors :
- Abnormalities in the sperm numbers, function, motility, structure (morphology) and anatomy cause male infertility. There are numerous causes :
- Genetic conditions – Klinefelter’s syndrome, cystic fibrosis
- Infections like Mumps, Gonorrhea, Chlamydia, interfere with sperm production or sperm health or can cause scarring that blocks the passage of sperm.
- Chronic illness like diabetes mellitus and renal disease
- Varicocele - it is a swelling of the veins that drain the testis. Relationship of mild and moderate varicocele to infertility is not well proved. It is one of the most common reversible cause of male infertility in patients where it is severe.
- Drugs such as cimetidine, antiandrogens, alcohol, anti-cancer medications.
- Undescended testicles: In some males, during fetal development one or both testicles fail to descend from the abdomen into the sac (scrotum) that normally contains the testicles. Decreased fertility is more likely in men who have had this condition.
- Exposure to environmental gonadotoxins, e.g. heat, smoking, metals, pesticides,
- Problems with sexual function — for example, difficulty with ejaculation or small volumes of fluid ejaculated, reduced sexual desire, or difficulty maintaining an erection (erectile dysfunction)
- Prior surgeries like vasectomy, inguinal hernia repairs, scrotal or testicular surgeries, prostate surgeries can cause damage and prevent sperm from being present in the ejaculate.
Is infertility becoming more common?
Yes, infertility is posing a greater challenge in today’s generation. It has become more common due to various reasons, the most important being late marriage and increasing age of the woman at first conception. The average age of conception now is about 29-30 years, whereas 20 years ago it was around 22-23 years. One in six to one in seven couples face the problem of infertility now.
Environmental and lifestyle factors like exposure to toxins, increasing use of plastic , smoking , stress , increasing BMI, poor nutrition, excessive alcohol is adding to this problem.
If you’re having trouble conceiving, or wish to delay pregnancy be aware of various options available to you. For this it is advisable to consult your doctor.
Does age affect fertility?
Age affects both female and male fertility although the effect on females is more profound.
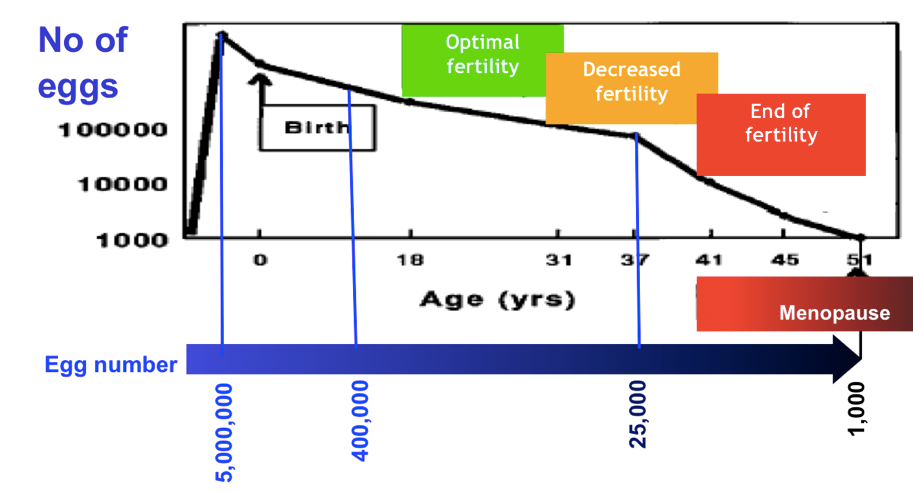
Women are born with a fixed number of eggs, which are about 7 million at 20 weeks of conception (when baby is in mother’s womb). This number reduces to 1-2 million at birth, and about 2-4 lacs at puberty, which continuously declines throughout the reproductive period till there are about 1000 at menopause. The age at which menopause is achieved is variable. In some women if this decay of eggs is fast one achieves an early menopause, whereas if it is slow the menopause may be late. Each, women has a biological clock which decides the number of eggs that will be recruited to grow and ovulate. Along with the number , the quality of eggs steadily declines as age advances and chance of miscarriages increases due to genetic abnormalities. The rate of clinically significant genetic abnormalities in live births rises from about 1/500 for women under 30, to 1/270 at age 30, 1/80 at age 35, 1/60 at age 40, and 1/20 at age 45.
Male fertility and ageing
Sperm quality deteriorates somewhat as men get older, but it generally does not become a problem before a man is in his 60s. There are some changes in fertility and sexual function in males as they age but not as abrupt or obvious as that in women Despite these changes, men in their 60s and 70s have fathered children with younger women. As men become older, their testes become smaller and softer, the sperm shape and motility tend to decline. Older men can have medical illnesses that adversely affect their sexual and reproductive function like decreased libido causing erectile dysfunction.
Hence women over the age of 35, should not wait for a year before seeking help from a fertility specialist.
Does stress cause infertility?
It is difficult to conclude how exactly stress impacts fertility , but reducing stress improves quality of life and in some ways increases chance of a treatment being successful. Some patients who are infertile react differently, some become aggressive and do multiple treatments and others isolate and distance themselves from their family and society. Both these situations negatively affect pregnancy and furthermore psychologically affect the couple. Moreover, stress can also result in sexual dysfunction in both partners.
Reducing stress level is important, it helps you to be able to cope with problems and make rational decisions, thus improving chance of treatment. Infertility treatment sometimes is stressful for couples. This stress can be reduced by talking to your doctor so they can reassure you about the treatment you are undergoing. Some other form of stress relieving therapy like acupuncture, yoga, music, meditation, mindfulness, visiting a counsellor or psychologist can also help cope with stress of infertility and improve overall health.
Can infertility be prevented?
Infertility to a certain extent can be prevented . Screening and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases can prevent infections which can damage the reproductive organs in both males and females. Knowledge and awareness about biological clock in females have been rampant nowadays. Social egg freezing is one of the most novel and life changing scientific advancement of our times where a woman can choose to freeze her eggs at a young age and have a baby at a later age. It makes woman be flexible about the time to reproduce and has been a boon .
Likewise , fertility preservation in men and women undergoing cancer treatment or surgery by way of sperm freezing and egg/embryo freezing, ovarian tissue freezing has helped many patients of cancer have children at a later age.
Avoiding smoking , excessive alcohol and substance abuse drugs can prevent infertility in both the partners. Hence improving lifestyle and environmental factors can help prevent infertility .
Can infertility be cured?
Yes , indeed infertility can be cured. It is always better to use the term sub-fertility rather than infertility. There are multiple options available today, which include newer drugs and protocols for ovulation induction, intrauterine insemination and assisted reproductive techniques (ART). Your fertility doctor can give you a comprehensive plan to address your problem and achieve pregnancy . The duration of treatment is sometimes lengthy and hence it is important for you to be patient for results. The treatment depends on the cause of infertility and can range from simple ovulation induction medicines to intrauterine inseminations (IUI) to more advanced treatment like In -Vitro feritilization (IVF) and intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection ( ICSI).
Visiting a doctor and being aware of what kind of treatment you need is necessary to overcome infertility.
GETTING THE DIAGNOSIS
When should we seek medical help?
You should seek medical help if
- You have been trying to conceive for over a year and have been unsuccessful
- You are above 35years of age and have tried naturally for a couple of months
- You have irregular periods, excessive heavy and painful periods, known conditions like PCOS, uterine fibroids , ovarian cysts, hypothyroidism.
- You are unable to have intercourse due to vaginismus, erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, ejaculatory problems or have infrequent intercourse due to travel or lack of time.
- You want to delay pregnancy and want to be aware of fertility preservation
- Known medical illness like Diabetes mellitus
- Smoking, excessive alcohol intake or intake of substance abuse drugs .
- It is important not to delay getting medical help in case you have trouble conceiving and taking an informed decision for future treatment .
Do we both need to be tested?
What tests will be advised in the first consultation?
At the first consultation a through history of both partners is taken, which includes past medical problems, social and family history and a detailed history of past tests and treatments if any is taken. This is followed by a clinical examination of the female partner and a trans vaginal ultrasound scan. This will prompt us to what test need to be done next.
Tests that are commonly done in the first consultation include
1. Husband semen analysis :. Semen analysis should be performed first as it is the easiest as well simplest and non-invasive test that rules out male factor. It evaluates parameters like the semen volume, sperm count, motility and morphology. The male also needs to be evaluated as they can account for about 50 % of the cause of infertility in the couple
2. Total motile sperm count (TMSC) TMSC is calculated by multiplying the concentration of sperm / ml (SC) x volume (ml) x motility divided by 100%. Sperm is normal if TMSC > 20 × 106 / ejaculate, lower values are considered as an abnormal semen analysis and define male infertility factor.
3. The doctor will advise you further treatment based on the semen analysis report.
4. Hormonal levels in the woman – TSH (for thyroid dysfunction) , Prolactin and AMH ( to test the women’s egg reserve)
5. Other Tests advised HSG ( Hysterosalpingography) - HSG is a radiological procedure to evaluate the shape of the uterine cavity, detect any intrauterine anomalies (polyp, fibroid, adhesions, septum) and test the patency of the fallopian tubes.
Please do show all your previous test results. Depending on how long back these tests were done and what the results are, some of the above tests could be omitted. Once the cause of the infertility is identified, the doctor will advise treatment protocols that will enhance the chance of you getting pregnant. If your age is more than 36 and you have been trying for > 3-4 years it is best to initiate therapy as quickly as possible. The choice of treatment the offered to you would depend on the cause and will be efficient and inexpensive as far as possible. For each diagnostic etiology, there is indeed a proper approach. Even after tests some infertility remains unexplained, but that does not mean that it cannot be treated successfully.
What is semen Analysis and how does it affect our fertility?
The male also needs to be evaluated as they can account for about 50 % of the cause of infertility in the couple. The semen analysis is a simple test which evaluates male fertility parameters like the semen volume, sperm count, motility and morphology.
Semen sample should be collected by masturbation after 2–4 days of abstinence in a wide-mouth sterile plastic container provided by the laboratory. The specimen should be collected in the ART clinic or pathology laboratory only. If collected at home, you need to sign an undertaking that the samle was collected at home and bought to the Lab for testing. If collected at home, the specimen should be kept at room or body temperature (should not be refrigerated) during transportation and examined preferably within 30- 60 minutes of collection.
A period of abstinence (period between sexual intercourse/night emission and masturbation) of 2-4 days is usually recommended but this is not an absolute prerequisite . Abstinence of < 2 days is accepted but that of more than 5 days is not recommended. If the abstinence is more the report may not show the actual values for count and motility. With increasing the abstinence the count is more and motility low.
The semen analysis should ideally be done in a standardized laboratory where quality control is assured. By standardizing protocols and methods in laboratories, it is possible to reduce the inter-laboratory variation . To achieve this purpose, doing the test according to the last edition of the "World Health Organization's Laboratory Manual on the testing and processing of human sperm" is recommended. Your treating doctor can guide you about where the test can be performed .
Normal values of semen analysis is as follows:
Parameter
|
Lower Reference Limit
|
Semen Volume
|
1.5 ml
|
Sperm concentration
|
15 million/ml
|
Total Sperm number
|
39 million/ejaculate
|
Progressive motility
|
32%
|
Total motility
|
40%
|
Vitality
|
58%
|
Sperm morphology, normal forms
|
4%
|
pH
|
>/= 7.2
|
Leucocyte
|
<1 million /ml
|
An abnormal semen analysis is when:
Sperm count is low - Oligozoospermia
Motility is below normal - Asthenozoospermia
Increased abnormal morphology - Teratozoospermia
All 3 parameters are affected - oligoasthenoteratozoospermia
Absence of Sperms - Azoospermia
No ejaculate - Aspermia
Total motile sperm count (TMSC)
TMSC is calculated by multiplying the concentration of sperm / ml (SC) x volume (ml) x motility divided by 100. TMSC > 20 × 106 / ejaculate is normal. If TMSC < 20 × 106 / ejaculate it is considered abnormal and may be responsible for male factor infertility.
The doctor will advise you further treatment based on the semen analysis report.
What is tubal patency test and how does it affect our fertility?
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is the commonest test performed for evaluation of tubal patency. It is a radiological procedure to evaluate the uterine cavity and patency with contour of the fallopian tubes.
This is a short OPD procedure done by injecting a dye into the cervix (mouth of the uterus) and then taking serial X-ray films. It is typically done in the post menstrual period (day 7 – 10 of the menstrual cycle). The presence of dye seen in the tube during its transit into the peritoneal cavity on both sides signifies patent fallopian tubes. Patency of the tubes is essential for natural conception and for treatments like IUI. The uterine cavity can be evaluated for presence of filling defects which can suggest fibroids, polyps or adhesions. Uterine septum or other congenital anomalies of the uterus can also be diagnosed by HSG. Depending on the result of the HSG, the doctor can suggest further treatment options for the couple.
How does thyroid affect my fertility?
How does raised prolactin affect my fertility?
What is AMH?
I have Low AMH, what’s next?
A low AMH would indicate a poor ovarian reserve, which means that the number of eggs left in the woman is lower than normal. It could be because of advancing age or it could even be seen in young women with premature ovarian insufficiency, when her ovaries age earlier than usual. The test can be repeated to confirm a low value. It also correlates with the Antral follicle count on the ultrasound scan, which denotes the number of eggs available for that cycle.
If you have a low AMH, you will be given tablets and injections to stimulate the growth of your eggs. This will be monitored on regular ultrasound scans and when the egg is mature, ie when the follicle is about 18 to 20 mm, an HCG injection will be given for rupture and after 36 hours, the washed motile sperms of your partner will be put inside your uterus with a small plastic catheter. Your partner has to provide the semen sample by masturbation. This procedure is called an IUI (Intrauterine Insemination). It will increase chances of you conceiving by 15 %. 3 cycles of IUI can be tried if you have a low AMH. If you do not conceive with that, the next plan of treatment for you will be to undergo IVF. At times if there is presence of some other factor for infertility or you are mor than 38 years old and have been trying to conceive for more than 3 years then IVF may be the first treatment of choice.
How is a polycystic ovary syndrome diagnosed? How would I know if I have PCOS?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition that affects a woman’s hormone levels resulting in either no ovulation or oligo-ovulation. Women with PCOS produce higher-than-normal amounts of male hormones and LH. This hormonal imbalance causes them to skip menstrual periods and makes it harder for them to get pregnant.
PCOS also causes hair growth on the face and body, and baldness. It can also contribute to long-term health problems like diabetes, high blood pressure, increased cholesterol and heart disease.
PCOS is a “syndrome,” or group of symptoms that affects the ovaries and ovulation. Its three main features are:
- Multiple small cysts (follicles) in the ovaries on pelvic ultrasound
- High levels of male hormones which can be detected clinically by presence of acne or hirsutism and also in the blood
- irregular or skipped periods
If you have any 2 out of the above 3, you may be diagnosed as PCOS.
Why is a transvaginal ultrasound necessary?
USG is a simple non-invasive test which is routinely recommended by the doctor to evaluate the pelvic pathologies like in the uterus and the ovaries. Abnormalities of the uterus such as fibroids, polyps, adenomyosis, uterine septum or other congenital anomalies can be picked up. The ovaries can be evaluated for size , presence of cysts , or polycystic morphology (PCOM )
The antral follicle count (AFC) is done on the day 2/3 of menses to know the woman’s egg reserve which is an important factor in the woman as a low ovarian reserve is a predictor of poor fertility.
Follicular monitoring by USG can be done to track the follicular development( growing egg ) in the ovary. It gives the doctor an accurate idea about ovulation (Release of egg)in the woman. At the same time, the lining of the uterus can be measured ( endometrial thickness) to know if the uterus is prepared adequately for implantation of the embryo.Follicular USG is also done routinely as part of fertility treatment in natural as well as assisted reproductive techniques.
What is Fibroid Mapping and why have I been advised that?
What is HysteroLaparoscopy and why have I been advised that ?
Hystero Laparoscopy is a surgery done in order to evaluate the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes , tubo ovarian relationship and peritoneum by laparoscopy and the uterine cavity from inside by hysteroscopy. It is performed under general anesthesia. Hysterolaparoscopy will be advised to you if your HSG test suggests a block in the tubes or if the ultrasonography suggests an abnormality in the uterus, uterine cavity, ovaries or if you are suspected to have endometriosis.
Through laparoscopy, which is putting a laparoscope with a camera inside the abdominal cavity to visualize the pelvic organs. Your doctor will be able to see the uterus for presence of any fibroid, adenomyosis and adhesions, the ovaries for presence of any cysts and endometriosis, and check for tubal patency, structure and surface of the tube and its relationship with the ovaries. A dye is put inside the uterus and if it seen coming out from the tubes, they are considered patent.
Laparoscopy will also be able to diagnose a condition called Endometriosis, which usually results in painful periods, sometimes painful intercourse and inability to conceive. This can also be treated by the Hystero Laparoscopy. The endometriotic deposits can be cauterized or removed and the chocolate cyst in the ovaries can be excised.
INTERPRETATION OF DIAGNOSIS
What is unexplained infertility? And what are the treatment options ?
Unexplained infertility is an idiopathic infertility i.e. the cause for infertility remains unknown in the presence of normal ovarian reserve, patent fallopian tubes, normal uterine cavity (the place wherein the pregnancy grows for 9 months) and normal semen factors.
Unexplained infertility can only truly be diagnosed after a complete fertility evaluation of the couple.
- You are ovulating regularly.
- Your ovarian reserve is good. (Evaluated with blood hormonal profile and/or ultrasound pelvis to look for antral follicle count.)
- Your fallopian tubes are open and healthy. (Evaluated with HSG or laparoscopy)
- Your partner’s semen analysis is normal (total count, sperm motility, and sperm shape.)
- Normal uterine cavity. (Evaluated with a 3 D Ultrasound pelvis and/ or hysteroscopy.)
Unexplained infertility can be seen in about 10 percent of the infertile couples and it is quite a frustrating diagnosis to receive. The incidence of unexplained decreases with more advanced teats being performed for evaluation. The good news is that there is still a 50 percent chance of getting pregnant naturally within a year following diagnosis especially in young couples with short duration of infertility.
The possible causes for unexplained infertility are:
- egg quality issues,
- tubal function issues despite patent tubes especially seen in females with chronic pelvic infection,
- sperm function issues
- issues with uterine receptivity (Important for implantation and sustaining the pregnancy)
The optimal treatment strategy needs to be based on individual patient characteristics such as
- age
- duration of infertility
- treatment efficacy
- side-effect profile
- cost considerations
The most common treatment map for unexplained infertility looks like this:
- 1. Lifestyle changes recommended (like weight loss through diet and exercise, stress management, quitting smoking and /or alcohol)
- 2. Continue to try on your own (if you’re young and willing) for six months to a year
- 3. Medicines like Clomiphene citrate or gonadotropins injections along with Intrauterine insemination (IUI) can be tried for three to six cycles
- 4. IVF treatment for three to six cycles if you fail to conceive with expectant management and IUI
- 5. (Rarely) third-party IVF treatments (like using an egg donor or surrogate)
I have a cyst what does that mean?
A cyst can form in either of your ovaries. The function of the ovary is to produce mature eggs every month during ovulation and to secrete hormones, namely estrogen and progesterone that vary according to the menstrual cycle.
You may not have any symptom as most cysts do not have any particular symptom. Some may present with pain, fullness, bloating or a lump if the size of the cyst is large enough to feel. If there is intense pain, it may indicate a twisting or torsion of the cyst which is a surgical emergency.
Most often, cysts are detected on a pelvic ultrasound incidentally. Most functional cysts and persistent corpus luteum seen on day 2 of the MC disappear on their own without treatment by the next cycle. The ultrasound will describe the characteristics of the cyst whether fluid filled or solid, its size. Based on that the type of cyst can be suspected however the final diagnosis is made when the cyst is sent for biopsy after removal.
Types of cysts – different types based on what cells they are formed from
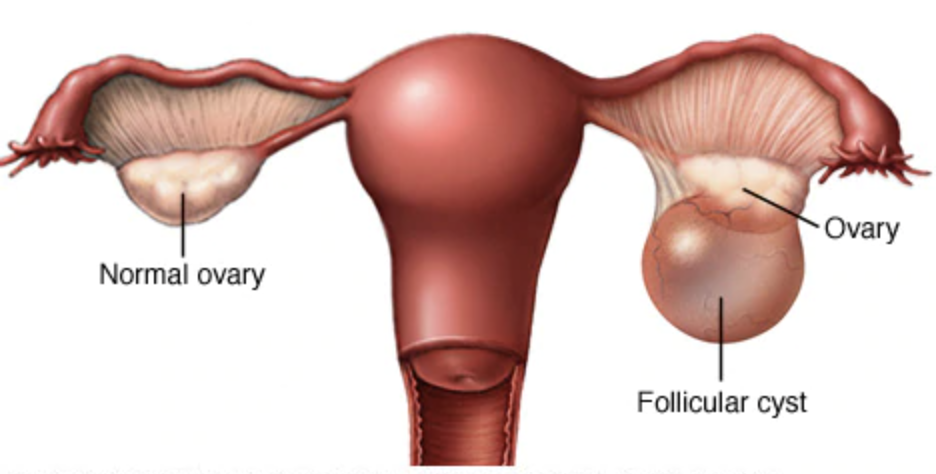
1. Functional cysts –
2. Follicular cyst
Corpus luteal cyst
These cysts are fluid filled which usually resolve by themselves or resolve after 2 to 3 months of oral contraceptive pills.
3. Dermoid - these can contain tissue, such as hair, skin or teeth, because they form from embryonic cells. They're rarely cancerous
4. Cystadenoma – serous, mucinous – develop from the surface of the ovary and filled with watery or mucinous content. They can be benign, borderline or malignant.
5. Endometriotic cyst – are present in a condition called endometriosis where the endometrium is present outside the uterus and bleeds when menses occur forming a chocolate cyst inside the ovary. This may present with pain, infertility and pain during having sex.
Dermoid and cystadenomas can become very large and can also lead to torsion.
Most cysts, other than functional cysts need surgical removal. Prior to surgery one needs to know the risk of malignancy. This is based on ultrasound findings and on tumour markers like Ca 125 and others which may indicate a malignancy, if high. The surgery is then planned accordingly.
If you have a cyst, you need to visit your gynaecologist to know the further course of action.
At times a fimbrial or para-ovarian cyst may be diagnosed as ovarian cyst.
What is endometriosis?
It could be present at various sites like the ovaries (chocolate cyst - comments site), peritoneum (lining covering the abdominal structures), between the vaginal wall and the rectal wall (lower part of the large bowel), in the uterus (adenomyosis), in and over the bladder, over the gut. Few rare sites like lungs, umbilicus, brain and nose also have been reported.
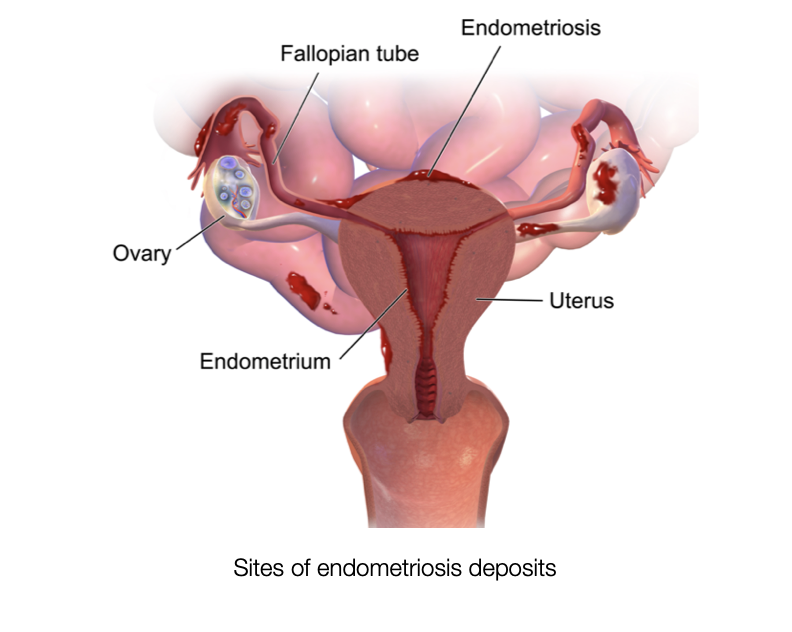
What explains the presence of endometriotic tissue outside the uterus?
There are many theories which attempt to explain the presence of endometrium outside the uterus.
- One of the most plausible theories is Retrograde menstruation in which there is flow of the blood along with the endometrium outside the uterus into the pelvis during the normal menstrual cycle. The endometrium then gets deposited either on the ovaries or peritoneum grow cyclically with every menstruation.
- Others include transformation of peritoneal tissue to endometrium through hormonal stimulation and/or immunological factors, which is termed as metaplasia.
- It may also be initiated by genetic causes and presence of stem cells. Stem cells have the ability to regenerate themselves into any kind of cell, for example, deposits of undifferentiated cells which turn into endometriotic deposits.
What are my options and my success rates of conceiving with endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a progressive disease which cause infertility due to distortion of tubes or tuboovarian relationship. It may also release certain toxic substances that may be harmful to the egg and sperm. The prevalence of endometriosis in subfertile women is up to 50%. The degree of infertility usually varies with the severity of endometriosis . The stages of endometriosis can be classified as following:
Women with endometriosis usually require some form of fertility treatment with Laparoscopic surgery or Assisted Reproductive Technology or a combination of both.
Women with Stage 1 and II endometriosis may conceive naturally. Women younger than 35 years and no other obvious cause of infertility in the couple, may try naturally for a period of 3 to 6months. If pregnancy does not occur in reasonable time, or there are other factors involved , they are advised to undergo fertility treatment.
Laparoscopic surgery with adhesiolysis and restoration of the tubo-ovarian anatomy has shown to be beneficial in these patients and may even improve the chances of natural conception. Laparoscopy also has the advantage of histological diagnosis of endometriosis. If women do not achieve pregnancy in 3 to 6 months of laparoscopy , they are offered intrauterine insemination ( IUI) with hormonal injections using Gonadotropins for a maximum of 3 cycles. Women with stage 1 and II endometriosis , especially if < 35yrs of age , have improved chance of pregnancy ( 15-18% success rates ) with IUI.
Women aged> 35 years and with low ovarian reserve are usually offered In Vitro Fertilisation ( IVF ) as the pregnancy rates are quite low with either only Laparoscopy or IUI combined with Gonadotropins.
The pregnancy rates with IVF are to the tune of 30-35% with each IVF cycle . This again is slightly lower than the those undergoing IVF for other reasons due to the various factors involved in endometriosis.
2. In Stage III or IV endometriosis , especially with large endometriotic (chocolate) cysts and severe pelvic pain , laparoscopy with cystectomy ( drainage of the chocolate fluid with removal of cyst wall ) of the endometriotic cyst and adhesiolysis with restoration of tubo ovarian anatomy may be advised . This may improve spontaneous conception rates. In patients who do not conceive within 3 months of surgery , IVF is recommended.
Some studies state that laparoscopic surgery and cystectomy may reduce the egg reserve due to iatrogenic damage to the ovarian follicles and hence may directly offer IVF for improving pregnancy rates. The success rates of either approach is up to 25% in both groups.
In these patients sometimes the fertility specialist may advise for IVF with freezing of embryos followed by either laparospcopic surgery or injections to suppress the pathology prior to embryo transfer. By doing the egg retrieval and embryo freezing prior to surgery , is to ensures good number of oocytes being retrieves and fertilized as at times post-surgery the ovarian reserve may be reduced and the number of oocytes retrieved would be less. Patients with Stage III or IV endometriosis have reduced pregnancy rates and may need multiple IVF cycles for achieving a live birth.
I have been diagnosed with Polycystic ovaries what are my options of planning a baby?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormone disorder that affects 5%-10% of women. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is the most common female hormonal reason for causing infertility.
The actual reason for PCOS is still unclear. It is a genetic environmental interaction that result in hormonal imbalance with menstrual abnormalities, excessive acne and hair growth and metabolic abnormalities like, diabetes mellitus, high blood preparation, dyslipidaemia and heart disease. There is increase in several male hormones present in our body with high insulin levels that are responsible for most of the symptoms of PCOS. The high male hormones and insulin levels can affect ovulation and metabolic function. When it affects ovulation, the release of the egg may not occur at all or occur as late as 25 – 40 days instead of 14 days from menstrual cycle.
It is certainly possible to get pregnant with PCOS:
- Talk with your doctor to know about the possible options to treat sub-fertility associated with PCOS.
- Your doctor will diagnose by ultrasound examination and clinical examination for presence of signs that suggest excessive male hormones and insulin levels. In case if only ultrasound signs are present in absence of clinical signs of excess male hormones and and insulin then your blood needs to be tested for the hormone abnormalities.. One needs to also do tour glucose tolerance levels and lipids.
- It is essential to study your ovulation pattern to ensure your pregnancy is successful and this can be easily done with the help of ultrasound.
- Lifestyle modifications remains the cornerstone for treating infertility related to PCOS. You need to follow a healthy balanced diet, incorporate regular physical activity in your lifestyle, and minimize stress. The aim is to reduce the body weight by 5 – 10% of the current status in obese PCOS and to restore the hormonal imbalance in both lean and obese PCOS.
- In some females who do not respond to the above management, your doctor will try to induce your ovulation through medicines (Tablets and/or injections) and monitoring it with ultrasound and thus guiding you with your fertile window
- Women with PCOS must be monitored carefully when these medicines are used to make sure that they are not over responding too much as this increases the risk of multiple births.
- Insulin resistance is seen in PCOS women and this also interferes with ovulation. Metformin which is an Insulin-sensitizing agent can help the body use insulin (blood sugar regulating hormone) more effectively to improve ovulation in some patients with PCOS. This may also lower the risk of developing diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
- If there are no results with above treatment in 3 to 4 months or there is an additional factor for infertility, then you may be advised to opt for advanced treatments like Intrauterine Insemination i.e. IUI or In-vitro fertilization i.e. IVF.
How does having Polycystic ovaries affect my chances of conceiving naturally as well as with treatment?
On average, women with PCOS take longer to become pregnant than other women. Polycystic ovaries generally happen due to hormonal imbalance. This hormonal imbalance leads to abnormal egg growth and ovulation. As a result, few females will have either no egg growth and ovulation or delayed egg growth and ovulation. Therefore, while planning a pregnancy with PCOS, it is important to know whether you are ovulating or not. This can be easily ascertained with the help of sonography.
The females who show delayed egg growth and ovulation can conceive naturally by finding out the timing of ovulation easily with the help of sonography.Those who do not show egg growth are investigated further to look out for the extent of hormonal imbalance. Lifestyle modifications with diet and exercise increases chances of correcting the hormonal imbalance and inducing ovulation will enhance the chance of conceiving naturally.
Fertility-Friendly Eating Tips for PCOS
- Eat a bigger breakfast and a smaller dinner.
- Include more protein and greens.
- When you eat carbohydrates, make them complex carbs (like whole grains and beans).
- Avoid junk, fried and packaged food
- If you eat sweets or a high carb food, combine it with healthy fats (avocado, olive oil, nuts) or protein to slow down the sugar spike.
- Avoid excess intake of tea and coffee
- No alcohol or smoking
However, there will still be females who might require fertility treatment.
The type of fertility treatment and success will depend on multiple factors:
- Age of the female
- Extent of PCOS
- Duration of infertility
- Any other cause of infertility
- Previous treatment history
- Body Mass Index (BMI)
Ovulation induction is usually the first medical treatment that a patient with PCOS seeking infertility treatment encounters. Ovulation induction involves the use of medication (like Tab Letrozole or Tab Clomiphene citrate with or without injectable gonadotropins and a trigger shot) to release the egg from the ovary. Ovulation induction using medications is generally effective and causes cumulative live birth rates of about 70%. If medications are successful in inducing ovulation, then fertility specialists may recommend starting a timed intercourse cycle for about 4 to 6 cycles depending on individual profile
For older patients or couples who have been unable to for a long period of time or who have not achieved success with above mentioned treatment, you will be recommended IUI or IVF instead of the routine ovulation induction with timed intercourse by your doctor.
Whai t s adenomyosis ?
Adenomyosis is a Gynaecological condition affecting the uterus in which the endometrial glands and stroma ( the tissue which lines cavity of the uterus) grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. This endometrium is functional and undergoes thickening , break down and bleeding during each menstrual cycle, leading to an enlarged , bulky uterus.
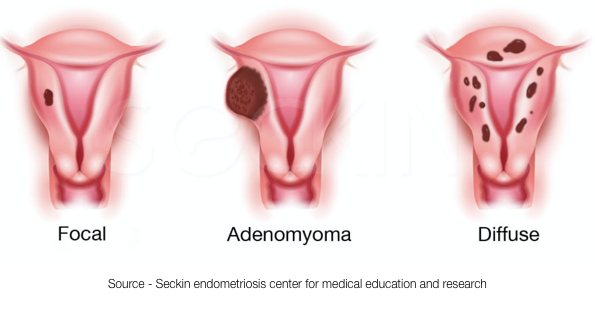
What are my treatment options with adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis is a poorly understood condition. Women with adenomyosis will sometimes have symptoms such as pelvic pain, pain with periods, irregular bleeding or heavy periods but sometimes they do not have any symptoms.Without treatment, adenomyosis may remain the same or symptoms can get worse.
Treatment is not necessary if a woman has no symptoms, is not trying to get pregnant, or is nearing menopause, which is when most women find relief from their symptoms.
However, there are many different treatment options available to women with this condition:
A. Medical treatment
Hormonal medications: Some hormonal treatments, such as oral contraceptive pills, progestin IUD’s, or injection (Depo-Provera), can help lessen the symptoms.
Injectable medications: GnRH agonists which are commonly used to treatment endometriosis by lowering estrogen levels have been used to treat adenomyosis. These medications can induce false or temporary menopause. These are only used for short-term and are not suitable for long-term use.
B. Uterine artery embolization: This involves placing a tube in a major artery in the groin and injecting small particles into the area affected by adenomyosis. This stops the blood supply reaching the affected area, which will shrink the adenomyosis and reduce symptoms. This has disadvantage in women who want to conceive. It can result in decreased egg pool and can also affect the inner lining of the uterus, which may then prevent attachment of the embryo.
C. Surgery for adenomyosis and infertility
This is certainly the most invasive and the riskiest option. In some cases portions of the uterus with focal or nodular adenomyosis has been removed and this has resulted in pregnancy . These are difficult surgeries to perform because adenomyosis does not have distinct borders that distinguish normal uterus from the adenomyosis so precise removal is challenging. This is obviously not an option for diffuse adenomyosis.
Hysterectomy is the only definitive treatment for adenomyosis is complete removal of the uterus.
What is Azoospermia? What are my treatment options?
i. Azoospermia is the medical term used when there are no sperm in the ejaculate. It can be “obstructive,” where there is a blockage preventing sperm from entering the ejaculate, or it can be “nonobstructive” when it is due to decreased sperm production by the testis.
ii.How common is azoospermia?

About 1% of all men and 10% to 15% of infertile men have azoospermia.
A normal sperm count is considered to be 15 million/mL or more. Men with low sperm counts (oligozoospermia or oligospermia) have a sperm concentration of less than 15 million/mL. If you have azoospermia, you have no measurable sperm in your ejaculate.
What are the causes of azoospermia?
- Obstruction in the reproductive tract due to-
- Trauma or injury to these areas.
- Infections.
- Inflammation.
- Previous surgeries in the pelvic area.
- Cystic fibrosis gene mutation. Nonobstructive causes include:
- Genetic conditions like Kallman’s syndrome, Klinefelters syndrome, Y gene deletion.
- Hormone imbalances/endocrine disorders, including hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
- Ejaculation problems such as retrograde ejaculation where the semen goes in to the bladder
- Testicular causes including testicular torsion, tumours
- Reactions to certain medications that harm sperm production.
- Radiation treatments.
- Diseases such as diabetes, cirrhosis, or kidney failure.
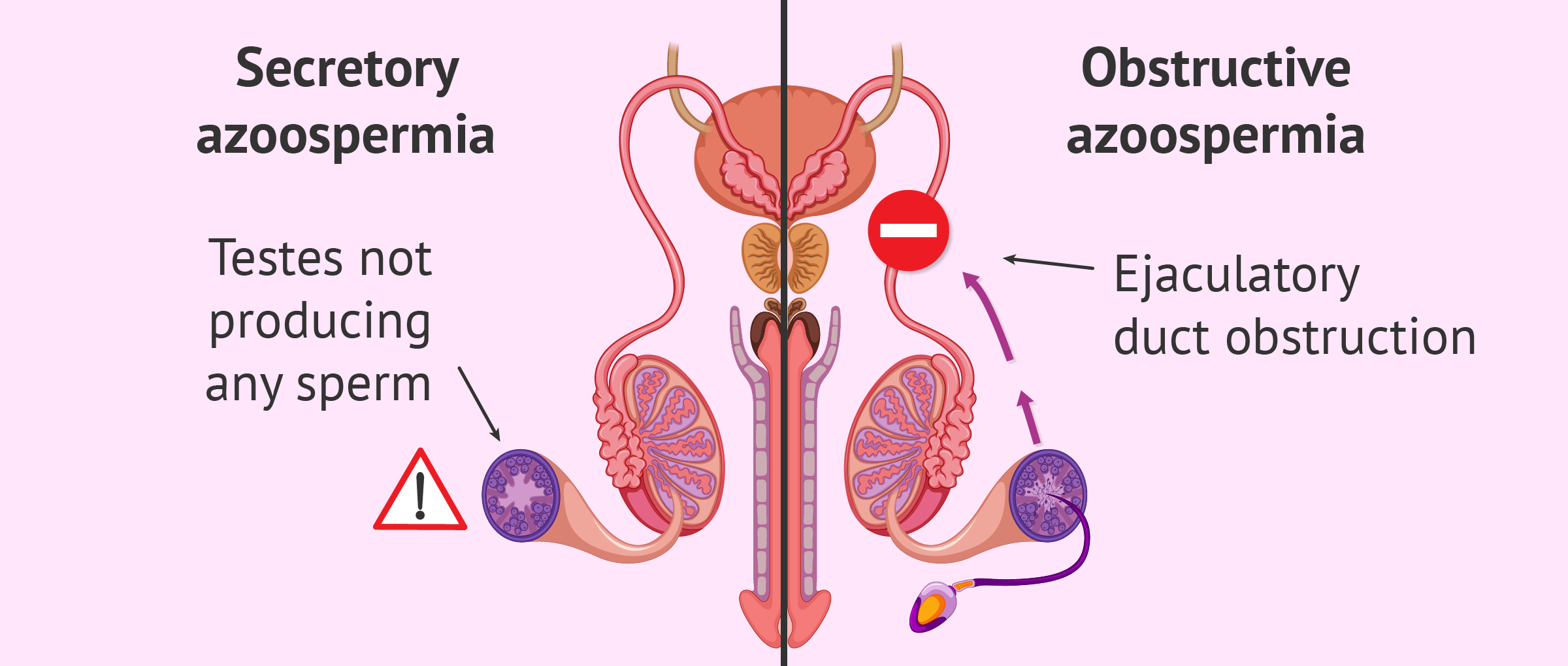
Treatment of azoospermia depends on the cause. Genetic testing and counseling are often an important part of understanding and treating azoospermia. Treatment approaches include:
i. Surgery can unblock tubes or reconstruct and connect abnormal or never developed tubes in case the azoospermia is caused by obstruction of the outflow tract.
ii. In case of low hormone production, you may be given hormone treatments. Hormones include follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) or tablets like clomiphene, tamoxifen and letrozole.
iii. If a varicocele is the cause of poor sperm production, the problem veins can be tied off in a surgical procedure, keeping surrounding structures preserved.
iv. Sperm can be retrieved directly from the testes or epididymis using PESA, MESA, TESE, TESA techniques.
v. Donor semen samples are obtained from ART semen banks and can be used after appropriate counselling and consent from the couple.
My tubes are blocked what next?
- Fallopian tubes are female reproductive organs that connect the ovaries and the uterus. It is also the site where the sperm meets the egg. If an egg is fertilized by sperm, it moves through the tube to the uterus for implantation.
- A blocked fallopian tube will prevent the passage for sperm to get to the eggs, as well as inhibit the transfer of the fertilized egg to the uterus.
- Common reasons for blocked fallopian tubes include:
o infection
o previous ectopic pregnancy
o past pelvic surgery
o pelvic adhesions - Generally, the tube patency is tested through imaging techniques like Hysterosalpingography (HSG) or sonosalpingography (SSG)
- If both tubes are fully blocked, pregnancy without treatment will be impossible. If the fallopian tubes are partially blocked, natural pregnancy can happen but there is increased chance of tubal ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy growing in the fallopian tube)
- If only one fallopian tube is blocked, the blockage most likely won’t affect fertility because an egg can still travel through the unaffected fallopian tube. But the time to pregnancy might be little longer. Fertility drugs with follicle monitoring and timed intercourse cycles can help increase your chance of ovulating on the open side and thus positive pregnancy outcomes.
- Treatment of infertility due to bilateral blocked tubes: Treatment options include:
i. Tubal surgery to correct the block: if the surgery is successful in terms of reversing the block, then the couple gets chance to conceive naturally.
ii. IVF: it will be a better option than surgery in following conditions:
• Severely damaged tubes not amenable to correction
• Severe distal tube blocks
• Female age more than 35
• Any other infertility factors
• Long duration of infertility
Comparing success rates with IVF with tubal correction surgery or Tubal Cannulation for proximal tubal block
Success rates are generally more favourable for IVF treatment, with approximately 60-65% per cycle pregnancy rates. Tubal surgery success rates are approximately 60-70% for correcting tubal blockages but pregnancy success rate is generally 25 -35%. The success rates of the surgery depends on location and type of blockage. Proximal tubal occlusion and mild distal blocks have higher success rates post-surgery. Although surgery can remove blockages, it doesn’t alter the functionality of tubes. Therefore, if the female doesn’t conceive naturally within one year of tubal corrective surgery, then IVF is the next choice of treatment.
I have a history of Tuberculosis, how does it affect my chances of conceiving?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by infection with the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis TB most commonly affects a person’s lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body and can cause serious illness TB can be cured with specific antibiotics.
Female genital tuberculosis (FGTB) is a Mycobacterium infection in the reproductive organs which often leads to chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, menstrual abnormalities and infertility.
Tb bacteria is transported by blood to other organs including reproductive organs and causes infection in fallopian tubes, uterus or in endometrial lining.
Tuberculosis has the ability to severely damage the fallopian tubes, it can further result in infertility. Also it may damage the endometrial lining and affect your chances of conceiving.Depending on the extent of damage the couple may be advised assisted reproductive techniques ranging from IUI to IVF to even surrogacy or adoption in cases where there is irreparable damage to the endometrium.
Apart from the tubes, TB also affects ovarian function. Depending upon the severity and stage of disease, there may be tubercles on the ovary, adhesions, caseation, tubo-ovarian cyst or abscess formation. It can reduce the blood supply to the ovaries resulting in a reduced ovarian reserve. Such women would at times need donor eggs to help them conceive.
Tuberculosis of the male reproductive tract can result in infertility. The infection can involve any part of the reproductive tract including the testis, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate and the ejaculatory ducts. Infertility usually results from the inflammation and scarring that follow the infection, resulting in distortion of the normal anatomy and causing obstruction. This will lead to Azpoospermia. Infertility may be the first presentation of genitourinary tuberculosis.
The diagnosis is done after detailed history and tests by doctor. The management depends on the site of obstruction and surgery is usually helpful. However, most other patients are candidates for in-vitro fertilization and have a good prognosis.
With early diagnosis, multiple regimens of treatment with standard four-drug regimen anti-tubercular drugs are used for a minimum of at least six to nine months. These help restore reproductive function and are favourable for fertility when tissue damage is minimal. Minimally-invasive laparoscopy may be needed for blocked fallopian tubes and hysteroscopic adhesiolysis or metroplasty to repair the uterine cavity damage.
Women without tubal or endometrial damage given early anti-tuberculosis treatment have a good chance of early spontaneous conception. Tuberculosis is associated with social stigma. Couple may be disheartened on diagnosis of tuberculosis which adds on the additional stress of difficulty in conceiving.
With advanced techniques and early diagnosis with prompt treatment with medicines there are better chances of conceiving after tuberculosis. In advanced cases, newer ART IVF techniques are useful with multiple options available for the couple including donor eggs and semen and Surrogacy.
How does having Diabetes affect my fertility and what are my treatment options?
Diabetes in men and women can affect their fertility and chance of having a baby. The risk of fertility problems is reduced when the diabetes is well managed. Diabetes can also result in sexual dysfunction especially in the male.
How can I prepare for pregnancy if I have diabetes?
Women and men who have diabetes should see their doctor for a review of their diabetes and a general health check, at least three to six months before trying to have a baby.
If you have diabetes, keeping your blood sugar levels as close to normal as far as possible before and during your pregnancy is important to stay healthy and have a healthy baby.
Your doctor will discuss ways to manage your diabetes to keep blood sugar levels in the healthy range during your pregnancy. This may involve:
- monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly
- creating a healthy eating plan
- some regular physical activity
- being in the healthy weight range
- reducing any stress or anxiety
- quit smoking
How can diabetes affect my baby?
A baby’s organs, such as the brain, heart, kidneys, and lungs, start forming during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy. High blood glucose levels can be harmful during this early stage and can increase the chance . of your baby having birth defects, such as heart defects or defects of the brain or spine.
High blood glucose levels during pregnancy can also increase the chance that your baby will be born preterm-too early, with higher baby weight, or low blood glucose right after birth. High blood sugar also can increase the chance that you will have a miscarriage or a stillborn baby.
What health problems could I develop during pregnancy because of my diabetes?
Hormonal and other changes in your body during pregnancy affect your blood sugar levels, so you might need to change how you manage your diabetes. Even if you’ve had diabetes for years, you may need to change your meal plan, physical activity routine, and medicines.
Pregnancy can worsen certain long-term diabetes problems, such as eye problems and kidney disease, especially if your blood sugar levels are too high. You also have a greater chance of developing preeclampsia, which is when you develop high blood pressure and too much protein in your urine during the second half of pregnancy. Pre-eclampsia can cause serious or life-threatening problems for you and your baby.
I have been diagnosed with SLE how does it affect my fertility what can I do next?
SLE is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks its own tissues-- causing inflammation and damage to organs. This disease can affect all the major organs-- as well as manifest on the skin in the form of a rash. There is no cure for SLE, but it can be treated with lifestyle adjustments and proper and adequate medication.
SLE tends to manifest when women are at their peak of fertility that is in their 20s and 30s. Most studies have found that because of the age of women when this disease manifests-- it can leave them at a higher risk of infertility and pregnancy complications. Women with this disease are considered to be having a “high risk” pregnancy.
Women with SLE may experience menstrual disturbances ranging from absolutely no periods to prolonged heavy bleeding in periods. Women who receive anti-coagulation therapy for thrombotic complications may also experience heavy periods . Delay in periods or loss of the egg pool may also occur as the result of cyclophosphamide (CYC) treatment, which may cause ovarian failure. Women with SLE may not get periods at all as a result of production of anti-corpus luteum antibodies with raised FSH levels. All in all women with SLE have an autoimmune- related menstrual dysfunction and any fertility treatment to be done needs to be planned meticulously with concordance with the opinion of a rheumatologist as well. If you become pregnant you may need to take heparin through out your pregnancy.
I have been diagnosed with Fibroids what next?
Uterine fibroids or leiomyomata are outgrowths of the uterine musculature and have a lifetime prevalence of 30% in women. They form the commonest group of benign tumors that affect women. They are hormone dependent and usually shrink after menopause. Fibroids may have no symptoms at all, but the commonest presenting complaint is heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding. Abdominal pain, dragging sensation in pelvis, constipation, urinary symptoms (pressure symptoms), difficulty to conceive, frequent miscarriages are other presentations.
The management of fibroids depends on their size, number, location and also the presenting complaint. From fertility point of view, it is mostly the submucosal type (projecting into the inner side of the womb) of fibroids or intramural (in the wall of the uterus) fibroids > 4 cms in size that need active management. Other type of fibroids such as smaller < 4 cms intramural fibroids or subserosal fibroids (outgrowths on outer surface of womb) usually do not diminish the chances of having a healthy baby and may not need any active treatment.
If you are planning a baby and have been diagnosed with fibroids, it would be best to seek a consultation with a fertility consultant/reproductive endocrinologist to confirm the best course of action in your condition.
What is cervical stenosis? How does it affect my fertility and what are the treatment option?
The cervix can vaguely be described as the mouth of the uterus. It is basically the part of the uterus that opens into the vagina and leads into the uterine cavity or the womb. Cervical stenosis is a condition in which the cervical canal is too narrow for the sperm to travel up to the fallopian tubes (where they meet and fertilize the egg). This condition usually arises due to formation of scar tissue inside the cervical canal secondary to conditions such as endometriosis, infections, radiation treatment etc.
In most fertility treatment (IUI or IVF), catheters need to passed through the cervix to access the womb in order to place either sperm or fertilized eggs inside the womb. In the presence of cervical stenosis, these procedures become too difficult and treatment options may include Dilatation of cervix under anesthesia or hysteroscopic procedures.
TREATMENT OPTIONS
What is timed intercourse ?How do I calculate my fertile period?
'Timed intercourse' is a practice of identifying the day of ovulation and, thus, the fertile period to increase the chances of getting pregnant. Whilst timed intercourse may increase conception rates and reduce unnecessary intervention and costs, there may be associated adverse aspects including the prolonged time taken to conceive and stress as a result of it. The methods used for ovulation prediction and timing intercourse include urinary hormone measurement (luteinizing hormone (LH), tracking basal body temperatures, cervical mucus changes (more liquid watery discharge) , calendar charting and ultrasonography.
The most popular method that is in vogue amongst couples trying to conceive in today’s internet era is to use ovulation predictor apps. These apps are basically a software that use the principles of the calendar method to calculate average length of menstrual cycles and also the longest cycle duration and the shortest cycle length. They then predict the days between which ovulation is mostly likely to fall on.
If you understand the principle on which the apps calculate the fertile period you will also be able to do it manually. Steps involved are as follows:
- Mark the first day of your period on a calendar as day 1 for at least 5-6 consecutive cycles.
- Count the total number of days between each cycle (the number of days between the first days of each period).You will get the shortest cycle and longest cycle duration
- Subtract 18 from the total number of days in the shortest cycle and mark that day as X.
- Subtract 11 from the total number of days in the longest cycle and mark that day as Y.
- The fertile period lies between X and Y
- Using this method is one of the ways of predicting ovulation. It is usually recommended to have intercourse on alternate days or daily in the fertile period.
What is Follicular Monitoring?
Follicular monitoring is a practice of doing a series of ultrasound scans to track the growth and eventual rupture of the follicle with release of egg. It must be borne in mind that an oocyte is not visible on ultrasound, hence follicle monitoring essentially relies upon picking up the act of follicle rupture to predict ovulation.
The process usually involves vaginal ultrasounds and involves a baseline ultrasound on day 2 followed by daily or alternate days from day 8 or 9 of menstrual cycle to determine the growth and rupture of the follicle.
What is IUI?
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment that involves placing washed sperms inside a woman's womb to facilitate fertilization. The aim of IUI is to accentuate the quality and number of sperms that reach the fallopian tubes and subsequently increase the chances of conception.
IUI involves a process called “sperm washing” that results in a concentrated amount of healthy sperm devoid of impurities. The doctor then uses a very thin catheter (long plastic tube) to put the sperm right into your uterus. IUI is usually less expensive than most other types of fertility treatments but it results in an increased chance of pregnancy
What is IVF?

In Vitro Fertilization or IVF is a type of fertility treatment where fertilization takes place outside the body. It’s one of the most successful treatments available for many people and is suitable for people with a range of issues.
The steps involved in IVF are as follows:
- Ovarian stimulation: process involves daily injections combined with follicular monitoring
- Egg retrieval: procedure to vaginally aspirate out eggs (oocytes) using sonographic guidance under anesthesia.
- Fertilization: Procedure done in lab that involves conventionally placing a specific concentration of separated and washed sperm around the egg in a petri dish allowing it to fertilize the eggs the lab.
- Embryo culture: The embryos are then grown in a tightly controlled laboratory environment inside a box called an incubator and are cultured for 2,3, 5 or 6 days (blastocyst stage).
- Embryo transfer: A catheter is used to place the embryos inside the womb
- Additional procedures- embryo freezing, luteal phase support etc.
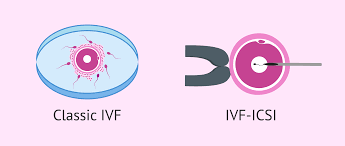
What is ICSI ?
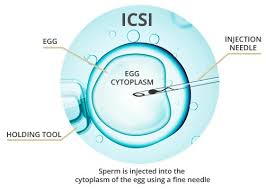
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is a procedure that involves holding a mature egg with a specialized pipette , and inject the sperm into the oocyte with a sharp needle. This sharp which is used to the immobilize sperm , aspirate it in the injection pipette and then inject it into the oocyte.
Is ICSI better than IVF?
Most controlled studies which have compared ICSI with and IVF have not shown any statistically significant differences in the results so it would be wrong to say ICSI is better than IVF. ICSI is usually recommended when there is a reason to believe that achieving fertilization may be difficult with IVF. ICSI is most commonly used with couples who are dealing with infertility due to severe male factors. Male infertility factors can include any of the following: low sperm counts, poor motility or movement of the sperm, poor sperm quality, sperm that lack the ability to penetrate an egg or azoospermia (absence of sperm).
In these specially indicated cases, ICSI definitely is a more successful procedure as compared to IVF. It may also be used when there was complete fertilization failure after IVF.
What is PICSI?
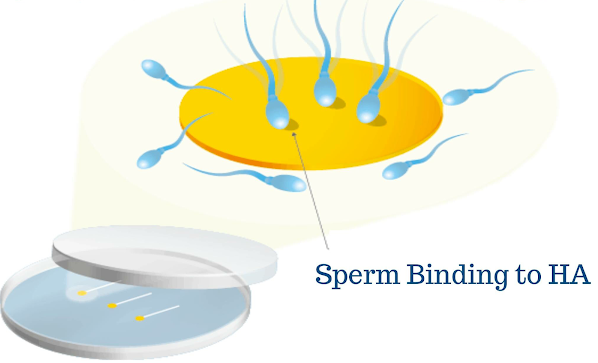
Physiological Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (PICSI) is a method of selecting the best possible sperm for fertilisation before injection into the egg. Sperms are placed in the PICSI dish containing samples of hyaluronan (a naturally occurring biopolymer found in all human cells) hydrogel.
What PICSI does is select sperm according to how well they bind to the hyaluronan which is normally present around an egg cell. Mature and functionally better sperms bind to the hyaluron and they are then isolated by the embryologist and used for ICSI.
PICSI is highly recommended in the following conditions though the evidence for its use is low:
- Previous failure or low fertilisation even after ICSI.
- Poor embryo quality or failure to develop (not related to poor egg quality).
- Recurrent miscarriages.
What is MACS?
What is IMSI?
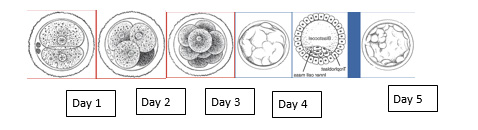
What is the difference between a Day 3 embryo Transfer and day 5. Embryo transfer? Which is better
An embryo begins its growth as a single cell, and then divides every 12-24 hours. By Day 3, it is about 8 cells, and is referred to as a multicell embryo. A day 3 embryo is still in cells form, where as a blastocyst or a day 5 embryo is when the embryo has grown and differentiated into the inner cell mass which will form the baby and the trophoblasts which will form the placenta
The progression from oocytes to day 5 embryo is a detrimental one. If we have 10 eggs hypothetically we will have 5 day 3 embryos and by day 5 may have only 2/3 left
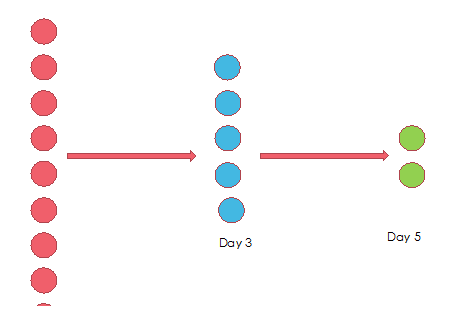
Each embryo that implants in a uterus needs to attain a day 5 status even if transferred at an earlier stage that is day 2 or 3. The benefit of taking the embryos to day 5 stays in the laboratory (in vitro) is that we know exactly which embryos have the potential to grow upto day 5 before we transfer them . And hence theoretically blastocyst transfer gives better pregnancy rates. However, your doctor and clinic will decide day 3 vs day 5 on various factors which you should consider discussing with your clinic
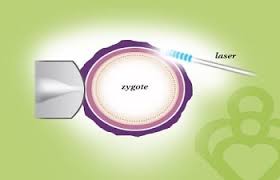
What is Laser Assisted hatching and why has it been advised to me? Does it really benefit me?
Laser-assisted hatching is a scientific IVF technique that can make it easier for the embryo to “hatch” or breakthrough its outer layer or “shell” (a membrane also known as the zona pellucida) by creating an opening. In some situations, this layer is abnormally thick and/or hardened with the freezing and thawing process among the contributing factors. The less difficulty the embryo has in hatching, the better its chance of attaching or implanting into the wall of the uterus.
Pregnancy cannot occur unless the embryo hatches and implants, and laser-assisted hatching can play a key role in achieving these crucial steps. The procedure involves sending a brief, strong light beam, under a microscope, to create a gap in the shell through which the embryo can come out.
However, whether you are a candidate for laser assisted hatching or not will be decided by your treating doctors
Common indications for laser assisted hatching are
1) Embryos created from oocytes of mother with advanced maternal age (they tend to have thick zona)
2) Freezing done by slow freezing those embryos tend to have thick zona
3) Repeated Implantation failure
What is embryo glue ? Is there any advantage of using it during embryo transfer
It’s an embryo transfer media that contains among other things, high levels of a special component called hyaluronan, also known as hyaluronic acid. Embryo glue is designed specifically for embryo transfer to ease the embryo’s adhesion to the mucous membrane of the uterus.
The special component in the glue helps the media wrap itself around the embryo and enhance its adhesion capabilities with the mucous membrane of Uterus due to the "sticky factor" of Hyaluronan.
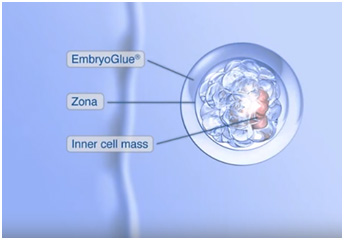
Indication - Recurrent Implantation Failure,
What is Pre-Implantation Genetic testing and who is it advised for?
Your embryos can be tested for abnormal chromosomes before they are transferred to the uterus. This is called preimplantation genetic testing, or PGT. It is done in a lab, using in vitro fertilization (IVF). One or more cells from each embryo is sent for genetic testing. Genetically healthy embryos are transferred to the uterus, where they may attach to its lining and produce a pregnancy.
PGT for monogenic disorders (PGT-M) determines whether you have a heritable genetic mutation that can be passed on to your children. PGT-M was previously called preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). This test looks for diseases caused by a mutation in a single gene, and it is offered to families with a known genetic mutation. That risk may have been discovered through routine genetic screening, such as carrier screening, or because one parent or family member already has a known genetic diagnosis.
PGT for aneuploidy (PGT-A) determines whether there are chromosomal abnormalities in your embryos, which can impact the chance of successful embryo implantation. This test was previous called preimplantation genetic screening (PGS). Chromosomes are packages of genes within cells. Extra or missing chromosomes can lead to miscarriage or a chromosomal syndrome like Down syndrome. These abnormalities happen randomly during embryo development and are not related to inherited genetic risks. PGT-A looks to see whether the embryos have all 46 chromosomes.
Both tests are done in conjunction with in vitro fertilization (IVF), but not everyone needs both tests. Your doctor and genetic counselor can guide you through the differences and which path is right for your family. Both PGT-A and PGT-M are done by removing five to 10 placental cells from the embryos created during IVF. The cells are examined for abnormalities based on which test you’re having, and healthy embryos are preserved for implantation.
What is donor egg IVF why has it been advised to me ?
Egg donation treatment is a process of creating an embryo in a test tube from a donor egg and your partner’s (donor) sperm, followed by replacing this embryo into your uterus. As a result of such egg donation treatment the chance of achieving pregnancy in your uterus and live birth is very high.
You might be a candidate for donor eggs if you have any of these conditions:
- Premature ovarian failure, a condition in which menopause has started much earlier than usual, typically before age 40
- Diminished ovarian reserve, meaning that the eggs that you have are of low quality; this can often be caused by age, because fertility drops off steeply after 40.
- Genetically transmitted diseases that could be passed on to your child
- A previous history of failure with IVF, especially when your doctor thinks that the quality of your eggs may be the problem
The use of donor eggs is becoming more common, especially among women over 40
What is Surrogacy and who is it for?
Surrogacy is an agreement in which a woman chooses to become pregnant through an embryo transfer and carry the resulting pregnancy for intended parents. It’s recommended that professionals be involved to guide both parties through the medical, legal and emotional processes.
There are a few different types of surrogacy: gestational vs. traditional, compensated or altruistic, and independent or agency-assisted.
A person who is waiting to become a parent via surrogacy is called an “intended parent.” Couples and individuals of all types may choose this path to parenthood, but most commonly, intended parents are:
- People who have struggled with infertility
- Prospective single parents
- Same-sex couples
- Anyone who is unable to safely carry a pregnancy to term

When are donor sperms used ?
Many women wish to have children but are unable to do so because their male partner is infertile, or they are single or have no male partner.
Couples use donor sperm (Donor Insemination) when the husband/partner has no sperm or a very poor semen analysis (azoospermia, oligospermia, poor motility), or when there is a genetic problem which could be inherited from the male. Single women who want a biological child also use DI, as well as LGBTQ couples also may consider using donor sperm as a means to conceive.
What are the implications of taking a single embryo transfer over a double embryo transfer and does it decrease my chances of conception?
ESET is elective Single Embryo Transfer, a process by which only one good quality blastocyst (or day 5) embryo is transferred into the uterus of the patient. The embryos that survive to the blastocyst stage of development are more likely to be strong and healthy. Blastocyst embryos have a much higher chance of implanting than 4 cell (day 2) or 8 cell (day 3) embryos, therefore fewer embryos are required to achieve a pregnancy.
“When you choose eSET, you are giving yourself the best possible chance for a safe pregnancy and a healthy baby.
Use of pre-implantation genetic diagnosis of aneuploidy and use of time lapse technology are used by many to improve the efficacy of eSET.
Is it mandatory that you have twins with IVF and what are the implications of having a twin pregnancy?
Having twins now is more common than it was in the past. According to a research twin birth have doubled over the last 40 years. The number of twin pregnancies is on rise and one of the reasons behind it may be the IVF treatment. Women have higher chances of twin pregnancy with IVF treatment if more than one embryo is transferred. At times one could have identical twin after IVF especially if blastocyst embryo has been transferred. Chances of twins in a normal pregnancy is around 6% while the chances of twins with IVF reaches up to 25%.
IVF treatment is not more than a blessing for many infertile couples across the globe. This medical process that increases the possibilities of a woman to conceive after she has tried for long naturally. In chances of twins with IVF, the doctor places the embryo (developed by the egg and sperm of the couple in an advanced laboratory) in the woman’s uterus where it will implant and grow.
MISCELLANEOUS
What is a trigger Injection ?
Women undergoing IVF treatment get a trigger shot so that eggs undergo changes to become mature before their collection.. These changes are required as all eggs are arrested in 46 chromosomes, and they have to become 23 before fertilization as the remaining 23 will come from the sperm.
The hormones most commonly used are human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) or luteinising hormone (LH) or GnRH agonist. In a spontaneous cycle it is increase in the LH levels which results in the initiation of changes in the oocyte but in an stimulated cycle we need to give an external trigger or injection 34-36 hours before oocyte retrieval to initiate these changes. Earlier we used only hCG trigger, but with this in the presence of many growing follicles there is a risk of ovaries hyper-responding with development of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Today with the use of GnRH agonist trigger we are able to totally or partially reduce the risk of OHSS.
So if you have a midday appointment for egg collection on Friday, you would take the trigger shot at midnight on the Wednesday prior.
What should I expect on the day of oocyte retrieval?
After about 34-36 hours post trigger either with hCG or GnRH agonist injection, egg retrieval will be performed under sedation or short general anesthesia . Intravenous medications will be given to prevent discomfort during the procedure. After medication your genitals will be cleaned with sterile normal saline and a needle will be placed through vagina into the ovary under Ultrasound guidance through the needle guide. You will not feel the pain of the procedure due to Injections given prior. The follicular fluid is collected (containing the eggs) in test tubes and passed to embryologists in IVF lab. After procedure you shall be transferred to recovery room. You will be informed about the number of eggs collected and whether IVF or ICSI is performed for fertilization.
What should I expect on day of Embryo Transfer ?
The embryo transfer typically takes place under sterile conditions, even though you will not be administered anesthesia. Embryologists will load the embryos into a special catheter. A speculum is placed into the vagina to allow visualization of the cervix, which will then be cleaned with normal saline and culture media. The mucus in the cervical canal also will be aspirated with a syringe. Abdominal ultrasound will help us locate the position of the embryo transfer catheter so that the embryos are transferred in the center of the cavity about 1.5 to 2 cms from the top of the uterine cavity. Once the position of the catheter has been identified ,the embryos are gently pushed or transferred into the uterus where they will hopefully implant
What precautions are to be taken in the period between embryo transfer and urine or blood test for pregnancy confirmation?
Usually post transfer it is recommended to take some amount of rest from routine work. Supportive medicines have to be taken as advised by your doctor. Try and distract yourself from anxiety related to test results. Unnecessary work maybe avoided during this period.
It is important to avoid swimming pools, spas and saunas for two weeks after embryo transfer. On the other hand, you can shower. Intensive exercise should be avoided but active movement (walking) is advisable. It is also important to keep yourself well hydrated
Why have I been prescribed so many medications after the embryo transfer till when will I have to continue these medications?
Injections used for stimulating the ovaries to obtain more eggs can reduce the production of important hormones required for implantation and progress of pregnancy. Medication post IVF are given to improve chances of implantation of transferred embryo, this requires supplementation of adequate quantities of progesterone support for proper implantation, Folic Acid tablets to prevent neural tube defects. All medications have to be continued till your fertility consultants have advised in your prescriptions.
Why have I been advised to meet a Psychological counsellor in the course of my treatment?
Infertility is a Stressful condition for some patients. You may or may not experience certain unavoidable questions arising in your mind before starting and during the treatment, post transfer of embryo and most important about the success rate and costs of treatment you are going to undergo. Several psychosocial and emotional factors may add up due to excessive web search which influence the outcome of your treatment. A psychological counsellors during the course of treatment may help you to understand better the treatment process as well as all queries that you have. This will help you in understanding of the situation and deal with it in a positive note.

